Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackEntropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- EntropyA measure of randomness or disorder in a system, related to the spread of energy at the atomic level.
- Isothermal ProcessA thermodynamic process where the temperature remains constant throughout.
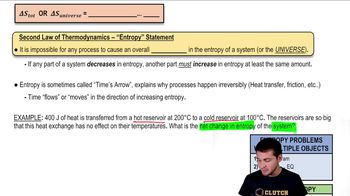
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsStates that the total entropy of a system or the universe can never decrease; it can only increase or remain constant.
- Heat TransferThe movement of thermal energy from a hotter object to a cooler one, increasing the entropy of the system.
- KelvinThe SI unit of temperature, used in thermodynamic equations to ensure consistency.
- Latent Heat of FusionThe heat required to change a substance from solid to liquid without changing its temperature.
- Phase ChangeA transition of matter from one state to another, such as from liquid to solid, involving energy transfer.
- RandomnessThe degree of disorder or unpredictability in a system, contributing to its entropy.
- Joules per KelvinThe unit of measurement for entropy, representing energy per unit temperature.
- Hot ReservoirA source of thermal energy at a higher temperature, often used in thermodynamic cycles.
- Cold ReservoirA sink for thermal energy at a lower temperature, receiving heat in thermodynamic processes.
- Delta SSymbol representing the change in entropy, calculated as heat transfer divided by temperature.
- Time's ArrowA concept describing the one-way direction of time, associated with the increase of entropy.
- FrictionA force that opposes motion, generating heat and increasing the entropy of a system.
- Energy SpreadThe distribution of energy within a system, influencing its level of entropy.