Electric Fields in Capacitors definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackElectric Fields in Capacitors definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
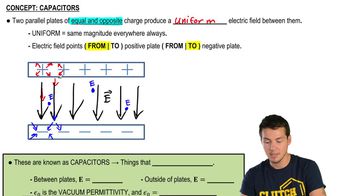
- CapacitorA device with two parallel plates holding equal and opposite charges, creating a uniform electric field.
- Electric FieldA region around charged particles where forces are exerted on other charges, uniform between capacitor plates.
- Vacuum PermittivityA constant denoted as epsilon_0, crucial for calculating electric fields in capacitors.
- Coulomb's ConstantA constant related to vacuum permittivity, used in electrostatic calculations.
- Uniform FieldA field with constant magnitude and direction, as seen between capacitor plates.
- ChargeThe property of matter that causes it to experience a force in an electric field, denoted as Q.
- AreaThe surface size of capacitor plates, affecting the electric field strength.
- Newton per CoulombThe unit of electric field strength, indicating force per unit charge.
- Parallel PlatesTwo plates in a capacitor that are equidistant and create a uniform electric field.
- Epsilon_0Symbol for vacuum permittivity, a fundamental constant in electromagnetism.
- Electric Field EquationE = Q / (epsilon_0 * A), used to calculate the field between capacitor plates.
- Zero FieldThe absence of an electric field outside the plates of a capacitor.
- Symmetric FieldField lines that cancel out due to symmetry, resulting in a uniform field.
- ConversionThe process of changing units, such as cm^2 to m^2, crucial in calculations.
- EpsilonA Greek letter representing permittivity in electric field equations.