Cyclic Thermodynamic Processes definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCyclic Thermodynamic Processes definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
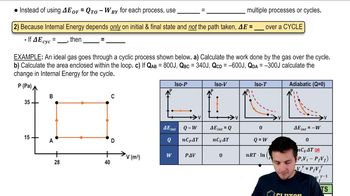
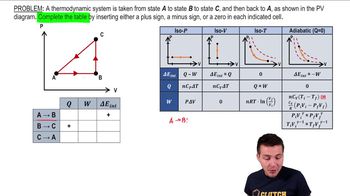
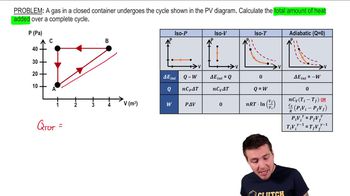
- Cyclic ProcessA sequence of steps returning a system to its initial state, with total work equal to the area enclosed on a PV diagram.
- PV DiagramA graph plotting pressure against volume, used to visualize thermodynamic processes.
- Isovolumetric ProcessA process with no change in volume, resulting in zero work done.
- Isobaric ProcessA process occurring at constant pressure, where work is calculated as pressure times change in volume.
- Internal EnergyThe total energy contained within a system, unchanged over a complete cycle.
- Heat TransferThe exchange of thermal energy between a system and its surroundings, equal to work done in a cycle with no change in internal energy.
- Clockwise LoopA path on a PV diagram where the work done is positive.
- Counterclockwise LoopA path on a PV diagram where the work done is negative.
- Work DoneThe energy transferred by a system during a process, represented by the area under the curve on a PV diagram.
- Delta EThe change in internal energy, zero for a complete cycle as it depends only on initial and final states.
- Area EnclosedThe region within a loop on a PV diagram, representing the total work done in a cyclic process.
- Ideal GasA theoretical gas whose molecules occupy negligible space and have no interactions, often used in thermodynamic calculations.
- Base Times HeightThe formula for calculating the area of a rectangle, used to find the area enclosed in a PV diagram.
- Positive WorkWork done by a system when a loop on a PV diagram is traversed clockwise.
- Negative WorkWork done by a system when a loop on a PV diagram is traversed counterclockwise.