Conservation of Energy in Rolling Motion definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackConservation of Energy in Rolling Motion definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
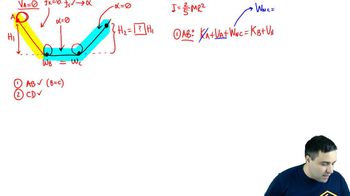
- Rolling MotionA type of motion where an object rotates around its axis while also translating along a surface.
- Static FrictionThe force that enables rolling motion by converting linear velocity into angular velocity without energy loss.
- Angular VelocityThe rate of rotation of an object, often denoted as omega, related to linear velocity in rolling motion.
- Moment of InertiaA measure of an object's resistance to changes in its rotation, crucial for calculating rotational kinetic energy.
- Rotational Kinetic EnergyThe energy due to an object's rotation, calculated using its moment of inertia and angular velocity.
- Translational Kinetic EnergyThe energy due to an object's linear motion, calculated using its mass and velocity.
- Conservation of EnergyA principle stating that total energy remains constant in a closed system, applied to both kinetic and potential energies.
- Potential EnergyThe energy stored due to an object's position, often related to height in gravitational fields.
- Solid CylinderA geometric shape with a specific moment of inertia, used in rolling motion problems.
- Inclined PlaneA flat surface tilted at an angle, used to study motion and energy conversion in physics.
- Linear VelocityThe rate of change of position of an object, related to angular velocity in rolling motion.
- RadiusThe distance from the center to the edge of a circular object, crucial in calculating angular velocity.
- CoefficientA numerical factor in equations, indicating the distribution of energy in rolling motion.
- HeightThe vertical distance an object is above a reference point, affecting its potential energy.
- AccelerationThe rate of change of velocity, requiring static friction in rolling motion to occur.