Combining Resistors in Series & Parallel definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCombining Resistors in Series & Parallel definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
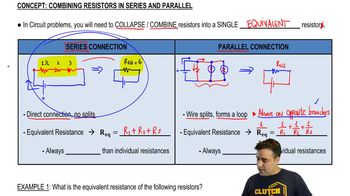
- Equivalent ResistanceA single resistor that represents the total resistance of a group of resistors in a circuit.
- Series ConnectionResistors connected end-to-end, increasing total resistance by summing individual resistances.
- Parallel ConnectionResistors connected across the same two points, decreasing total resistance by providing multiple paths for current.
- Direct ConnectionA connection between resistors without any splits in the wire, characteristic of series circuits.
- LoopA closed path in a circuit where current can flow, often used to identify parallel connections.
- Voltage SourceA component, like a battery, that provides electrical energy to a circuit.
- CurrentThe flow of electric charge through a conductor, influenced by the circuit's resistance.
- OhmThe unit of electrical resistance, symbolized by Ω, representing the resistance between two points.
- Common DenominatorA shared multiple of the denominators of two or more fractions, used to simplify parallel resistance calculations.
- Shortcut EquationA simplified formula for calculating equivalent resistance in specific resistor configurations.
- BranchA part of a circuit where the current can split into different paths, relevant in parallel circuits.
- ChargeAn electrical property of particles that causes them to experience a force in an electric field.
- Resistor NetworkA combination of multiple resistors in a circuit, which can be simplified to a single equivalent resistor.
- FractionA mathematical expression representing the division of one quantity by another, used in parallel resistance calculations.
- SimplificationThe process of reducing a complex resistor network to a simpler form with fewer components.