Collisions with Springs definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCollisions with Springs definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
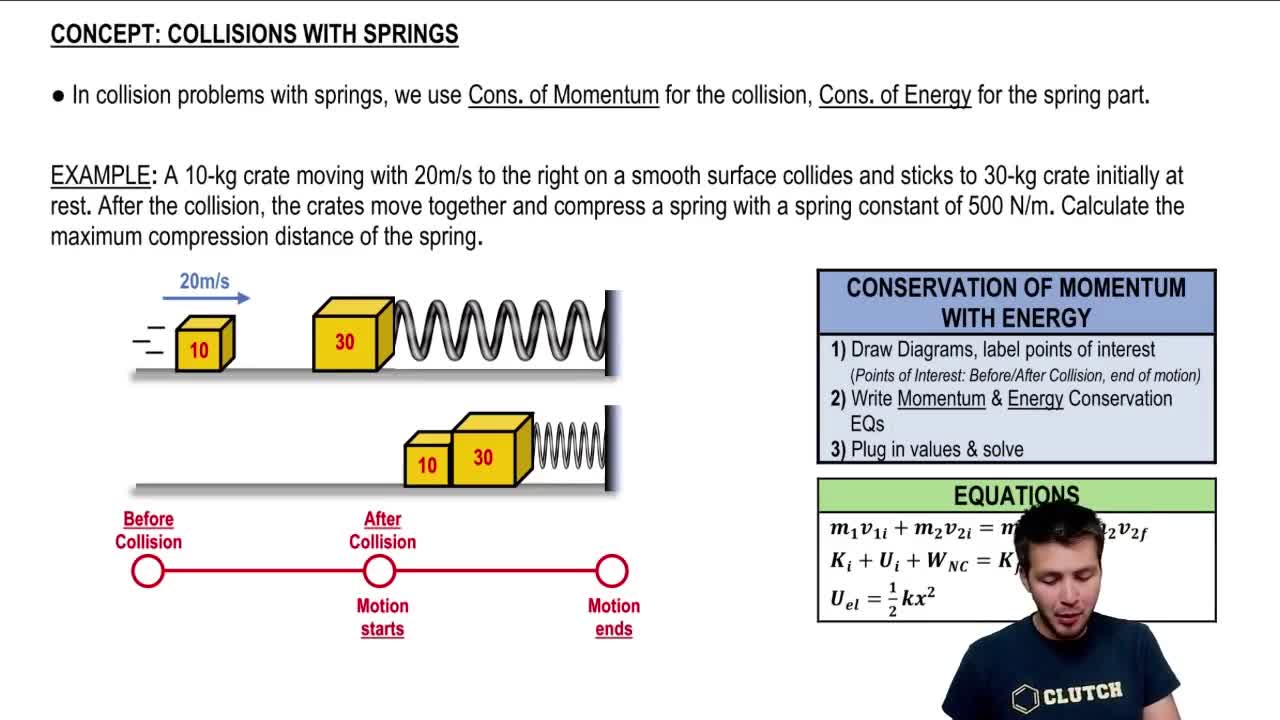
- CollisionAn event where two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time.
- MomentumA measure of the motion of a body, equal to the product of its mass and velocity.
- Conservation of MomentumA principle stating that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant if no external forces act on it.
- EnergyThe capacity to do work, which can exist in various forms such as kinetic or potential.
- Conservation of EnergyA principle stating that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant over time.
- Kinetic EnergyThe energy possessed by an object due to its motion, calculated as 1/2 mv^2.
- Potential EnergyThe energy stored in an object due to its position or configuration.
- Elastic Potential EnergyEnergy stored in elastic materials as the result of their stretching or compressing.
- Spring ConstantA parameter that describes the stiffness of a spring, denoted as K in Hooke's Law.
- Inelastic CollisionA type of collision where the colliding objects stick together after impact.
- Maximum CompressionThe greatest distance a spring is compressed from its relaxed position.
- Square RootA value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number.
- MassA measure of the amount of matter in an object, typically in kilograms.
- VelocityThe speed of something in a given direction.
- FrictionThe resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another.