Circular Motion of Charges in Magnetic Fields definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCircular Motion of Charges in Magnetic Fields definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
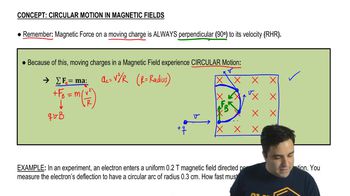
- Magnetic ForceA force experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field, always perpendicular to the velocity.
- Right-Hand RuleA method to determine the direction of magnetic force on a positive charge moving in a magnetic field.
- Centripetal ForceThe inward force required for an object to move in a circular path, provided by magnetic force in this context.
- Centripetal AccelerationAcceleration directed towards the center of a circular path, calculated as v squared over r.
- RadiusThe distance from the center to the edge of the circular path of a charge in a magnetic field.
- MomentumThe product of mass and velocity, represented as mv, crucial in deriving the radius equation.
- Helical MotionThe spiral path of a charge moving at an angle to a magnetic field, combining circular and linear motion.
- Uniform FieldA magnetic field with constant magnitude and direction, affecting the motion of charges uniformly.
- TeslaThe unit of magnetic field strength, symbolized as T, used in calculating the force on a charge.
- Sine of ThetaA trigonometric function used in calculating magnetic force, with theta as the angle between velocity and field.
- Circular ArcA segment of a circle's circumference, used to describe the path of a charge in a magnetic field.
- DisplacementThe change in position of a charge, tangential to the circular path in a magnetic field.
- CoulombThe unit of electric charge, symbolized as C, used to quantify the charge of particles like electrons.
- VelocityThe speed and direction of a moving charge, crucial in determining the radius of its circular path.
- Speed of LightThe maximum speed limit in the universe, used as a reference to check the reasonableness of calculated velocities.