Capacitors in AC Circuits definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCapacitors in AC Circuits definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- CapacitorA device that stores electrical energy in an electric field, used in AC circuits to influence current and voltage.
- AC CircuitAn electrical circuit powered by alternating current, where the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction.
- VoltageThe electric potential difference between two points, influencing the flow of current in a circuit.
- CapacitanceThe ability of a capacitor to store charge per unit voltage, measured in farads.
- ChargeThe amount of electric charge stored on a capacitor, influencing the voltage across it.
- CurrentThe flow of electric charge in a circuit, measured in amperes, and influenced by voltage and resistance.
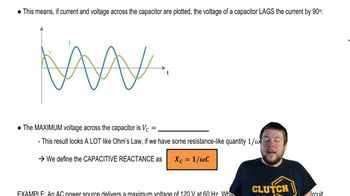
- Capacitive ReactanceA resistance-like quantity in AC circuits, inversely proportional to frequency and capacitance.
- OmegaThe angular frequency in an AC circuit, calculated as 2π times the frequency.
- FrequencyThe number of cycles per second in an AC circuit, measured in hertz.
- Ohm's LawA principle stating that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it.
- ResistanceA measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit, measured in ohms.
- ReactanceThe opposition to the change in current flow in an AC circuit, combining resistance and capacitive effects.
- Phase AngleThe angular difference between the voltage and current waveforms in an AC circuit.
- ImpedanceThe total opposition to current flow in an AC circuit, combining resistance and reactance.
- Kirchhoff's Loop RuleA principle stating that the sum of the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit must equal zero.