Intro to Calorimetry definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntro to Calorimetry definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
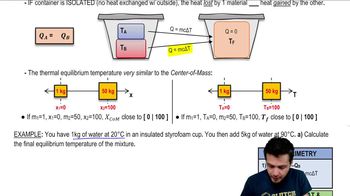
- CalorimetryThe study of measuring heat transfer during physical and chemical processes.
- Thermal EquilibriumA state where two or more materials reach the same temperature and no heat flows between them.
- Heat TransferThe movement of thermal energy from a hotter object to a cooler one.
- Insulated ContainerA vessel that prevents heat exchange with the external environment.
- Specific HeatThe amount of heat required to change the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius.
- MassThe quantity of matter in an object, often measured in kilograms in calorimetry problems.
- TemperatureA measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance, influencing heat transfer.
- Equilibrium TemperatureThe final uniform temperature reached by materials in thermal equilibrium.
- Heat ConservationThe principle that total heat remains constant in an isolated system during heat transfer.
- Delta TThe change in temperature, calculated as final temperature minus initial temperature.
- AlgebraA branch of mathematics used to solve equations, crucial in deriving calorimetry formulas.
- Center of Mass AnalogyA comparison used to explain how equilibrium temperature skews towards the mass with higher heat.
- Heat EquationAn expression used to calculate heat transfer, often in the form Q = mcΔT.
- Negative SignIndicates the direction of heat flow, showing heat loss in calorimetry equations.
- Plug and ChugA method of solving equations by substituting known values into a formula.