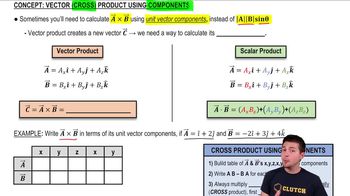
Calculating Cross Product Using Components definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCalculating Cross Product Using Components definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Cross ProductA vector operation that results in a vector perpendicular to two given vectors.
- Unit VectorA vector with a magnitude of one, used to indicate direction.
- ComponentsThe projections of a vector along the axes of a coordinate system.
- i, j, kUnit vectors along the x, y, and z axes, respectively.
- Vector NotationA representation of vectors using unit vectors i, j, and k.
- Table MethodA systematic approach to calculate cross products using repeated components.
- Diagonal MultiplicationA technique in the table method involving crosswise multiplication of components.
- AB - BA PatternA mnemonic for calculating cross product components by subtracting reverse products.
- Cx, Cy, CzThe x, y, and z components of the resulting cross product vector.
- Plug and ChugA method of substituting values into a formula to compute results.
- Negative Sign HandlingCareful management of negative signs in calculations to avoid errors.
- Scalar ProductA product of two vectors resulting in a scalar, also known as dot product.
- Perpendicular VectorA vector that is at a right angle to a given plane or vector.
- Generic EquationA formula that represents a general case, applicable to various specific instances.
- Pattern RecognitionIdentifying consistent sequences or structures in mathematical operations.