Buoyancy & Buoyant Force definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackBuoyancy & Buoyant Force definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
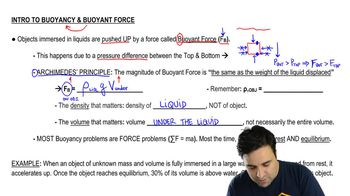
- BuoyancyThe phenomenon causing objects to float or rise in a liquid due to pressure differences.
- Buoyant ForceThe upward force exerted by a fluid on a submerged object, equal to the weight of the fluid displaced.
- Archimedes' PrincipleStates that the buoyant force on a submerged object is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced.
- DensityThe mass of an object divided by its total volume, crucial for solving buoyancy problems.
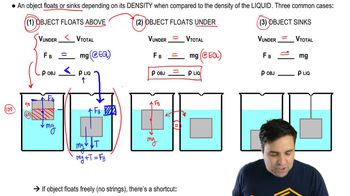
- EquilibriumA state where the net force is zero, often occurring when buoyant force equals gravitational force.
- Apparent WeightThe weight of an object in a fluid, affected by buoyant force, measured by tension or normal force.
- Pressure DifferenceThe variation in pressure between the top and bottom of a submerged object, causing buoyant force.
- Volume SubmergedThe portion of an object's volume that is underwater, crucial for calculating buoyant force.
- Normal ForceThe force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object resting on it, often counteracting gravity.
- TensionThe force transmitted through a string or cable when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends.
- Gravitational AccelerationThe acceleration due to gravity, typically 9.8 m/s² on Earth, used in buoyancy calculations.
- Liquid DensityThe mass per unit volume of a liquid, a key factor in determining buoyant force.
- FloatingThe condition where an object remains on the surface of a liquid due to its lower density.
- SinkingThe condition where an object descends in a liquid due to its higher density compared to the liquid.
- SuspendedThe state where an object remains submerged but does not sink or rise, having equal density to the liquid.