Equilibrium in 2D definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackEquilibrium in 2D definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
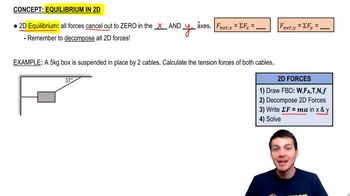
- EquilibriumA state where all forces acting on an object cancel out, resulting in zero net force.
- Free Body DiagramA visual representation of all forces acting on an object, used to analyze equilibrium.
- Tension ForceThe pulling force transmitted through a string, cable, or rope when it is pulled tight.
- Weight ForceThe force due to gravity acting on an object's mass, directed downwards.
- Trigonometric FunctionsMathematical functions like sine and cosine used to decompose forces into components.
- ComponentsThe parts of a force acting along the x and y axes, derived using trigonometry.
- CosineA trigonometric function used to find the adjacent side of a right triangle.
- SineA trigonometric function used to find the opposite side of a right triangle.
- Net ForceThe overall force acting on an object, calculated as the vector sum of all forces.
- NewtonThe SI unit of force, symbolized as N, representing the force needed to accelerate 1 kg by 1 m/s².
- MagnitudeThe size or length of a vector, representing the amount of force without direction.
- AngleThe measure of rotation needed to bring one line or plane into coincidence with another.
- AxisA reference line used in a coordinate system to determine the position of points.
- DecompositionThe process of breaking a force into its x and y components using trigonometry.
- DiagramA simplified drawing showing the appearance, structure, or workings of something.