21. Kinetic Theory of Ideal Gases
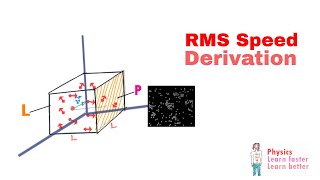
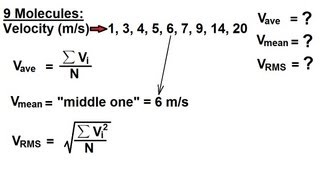
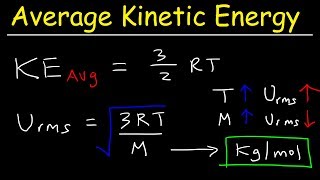
Root-Mean-Square Velocity of Gases
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
What is the temperature of a sample of CO2 molecules whose rms speed is 300 m/s? The molecular mass for Carbon and Oxygen is 12.01 g/mol and 16 g/mol, respectively.
586views3rank - Textbook Question
Oxygen (O2) has a molar mass of 32.0 g/mol. What is (g) How many oxygen molecules traveling at this speed are necessary to produce an average pressure of 1 atm?
1190views - Textbook Question
Oxygen (O2) has a molar mass of 32.0 g>mol. What is (e) Suppose an oxygen molecule traveling at this speed bounces back and forth between opposite sides of a cubical vessel 0.10 m on a side. What is the average force the molecule exerts on one of the walls of the container? (Assume that the molecule's velocity is perpendicular to the two sides that it strikes.)
746views - Textbook Question
For diatomic carbon dioxide gas (CO2, molar mass 44.0 g/mol) at T = 300 K, calculate (c) the root-mean-square speed v_rms.
975views - Textbook Question
Smoke particles in the air typically have masses of the order of 10-16 kg. The Brownian motion (rapid, irregular movement) of these particles, resulting from collisions with air molecules, can be observed with a microscope. (a) Find the rootmean-square speed of Brownian motion for a particle with a mass of 3.00 * 10-16 kg in air at 300 K.
1619views