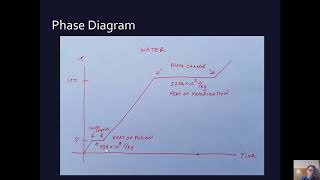
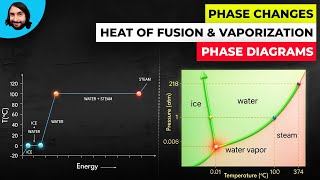
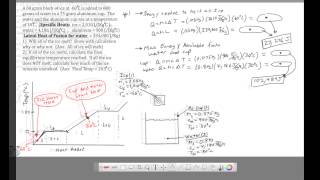
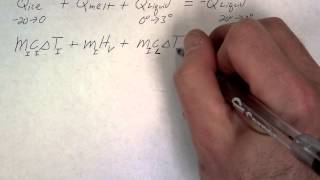20. Heat and Temperature
Calorimetry with Temperature and Phase Changes
20. Heat and Temperature
Calorimetry with Temperature and Phase Changes
Additional 4 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Practice this topic
- Textbook Question. A vessel whose walls are thermally insulated contains 2.40 kg of water and 0.450 kg of ice, all at 0.0°C. The outlet of a tube leading from a boiler in which water is boiling at atmospheric pressure is inserted into the water. How many grams of steam must condense inside the vessel (also at atmospheric pressure) to raise the temperature of the system to 28.0°C? You can ignore the heat transferred to the container.639views2rank
- Textbook Question
A 4.00-kg silver ingot is taken from a furnace, where its temperature is 750.0°C, and placed on a large block of ice at 0.0°C. Assuming that all the heat given up by the silver is used to melt the ice, how much ice is melted?
707views - Textbook Question
An insulated beaker with negligible mass contains 0.250 kg of water at 75.0°C. How many kilograms of ice at -20.0°C must be dropped into the water to make the final temperature of the system 40.0°C?
2199views2rank - Textbook Question
(II) High-altitude mountain climbers do not eat snow, but always melt it first with a stove. To see why, calculate the energy absorbed from your body if you
(a) eat 1.0 kg of -15°C snow which your body warms to body temperature of 37°C;
190views - Multiple ChoiceWhat is the mass of the ice cube initially taken from the freezer, given that the final temperature of the system is 17.0 °C?37views
- Multiple ChoiceWhat mass of steam at 100°C must be added to 1.90 kg of ice at 0°C to yield liquid water at 16°C? The heat of fusion for water is 333 kJ/kg, the specific heat is 4186 J/kg°C, and the heat of vaporization is 2260 kJ/kg.30views