24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
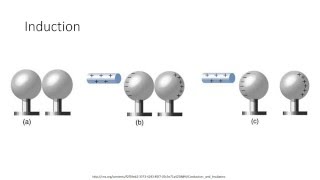
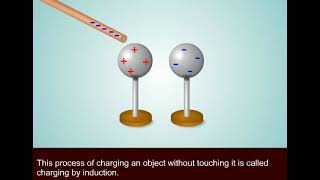
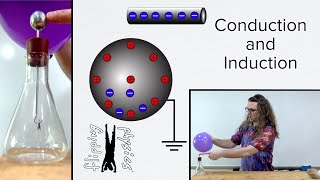
Charging Objects
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceA certain electroscope is charged until it holds of negative charge. Have electrons been added to the electroscope, or removed from it, and how many?1055views2rank
- Textbook Question
A plastic rod that has been charged to −15 nC touches a metal sphere. Afterward, the rod's charge is −10 nC. How many charged particles were transferred?
1269views - Textbook Question
A plastic rod that has been charged to −15 nC touches a metal sphere. Afterward, the rod's charge is −10 nC. What kind of charged particle was transferred between the rod and the sphere, and in which direction? That is, did it move from the rod to the sphere or from the sphere to the rod?
884views - Textbook Question
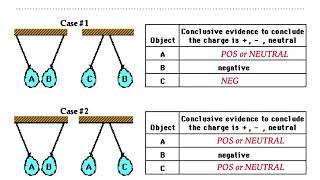
Figure 22.8 showed how an electroscope becomes negatively charged. The leaves will also repel each other if you touch the electroscope with a positively charged glass rod. Use a series of charge diagrams to explain what happens and why the leaves repel each other.
1473views - Textbook QuestionA plastic rod that has been charged to −15 nC touches a metal sphere. Afterward, the rod's charge is −10 nC.b. How many charged particles were transferred?752views
- Multiple Choice
Why does a glass rod become when it is rubbed with a silk cloth?
73views - Multiple Choice
When an object becomes charged, which of the following best describes what has happened to the object?
118views - Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes results in an object becoming electrostatically charged?
104views