- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

A tsunami generates two types of waves: a primary wave that travels at 200 m/s and a secondary wave that travels at 100 m/s. If a warning system detects these waves arriving 15 minutes apart, calculate the distance from the tsunami's origin to the detection point.
You are adjusting the tension in a stretched copper wire so that the velocity ratio of longitudinal waves to transverse waves is equal to 5. The cross-sectional area of the copper wire is 1 mm2 and the Young modulus of copper is 1 × 1011 Pa. Find the tensile stress (σ) in the wire.
When the atmospheric temperature is 0 °C, a vibrating rod mounted on a hot air balloon generates longitudinal waves traveling at a speed of 331 m/s. The vibrating rod's frequency is 1000 Hz. The hot air balloon rises in the sky. At a height where the temperature is T, the waves have a wavelength of 0.28 m. To obtain this wavelength, what should be the atmospheric temperature? Consider air as an ideal gas.
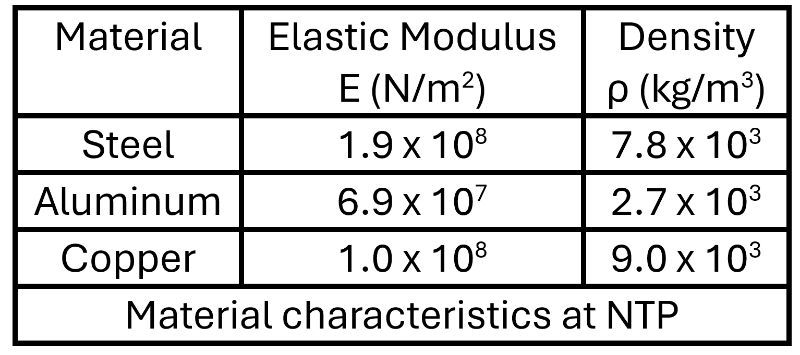
A sound wave travels through a railway track made of steel. From the table below, estimate the speed with which sound travels through the railway track.
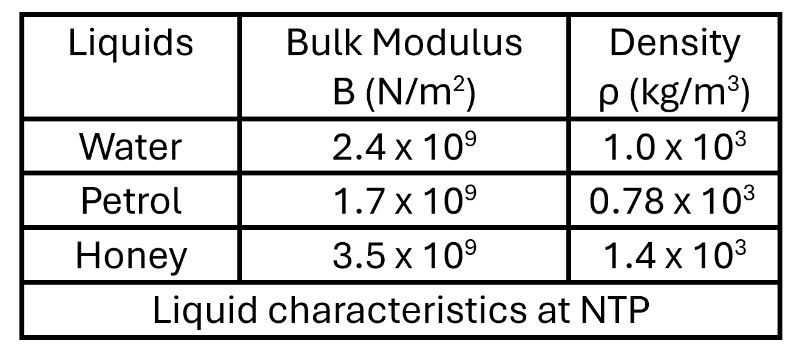
A sonar system on a ship makes a signal in the water and receives an echo (that bounced off the ocean floor) of the signal back after 3.5 s. Making use of the table given below, find the depth of the sea.
Imagine a longitudinal wave traveling through a steel rod. The wave has a frequency of 8000 Hz. What is the wavelength of this wave as it propagates through the steel rod?