- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Consider a person placing a 1.5 cm-thick vegetable oil layer on a horizontal glass surface. A laser beam in the air strikes the oil at 40° from normal. What direction, measured as an angle from normal, does the laser beam travel when it enters the glass? (Assume the refractive index of oil is 1.47 and for glass is 1.50).
A researcher is investigating a solution in a petri dish. They shine a beam of light at a 55° angle to the normal from the air onto the solution. The beam refracts inside the solution and continues at a 37° angle to the normal. Determine the solution's refractive index.
Consider a ruby cube with a refractive index 1.76 dropped into a water pool. A light beam in the water hits the ruby surface at an incidence angle of 30°. Determine the beam's angle relative to the ruby's surface after entering the crystal.
A greenhouse uses glass panes with a thickness of 3.0 mm. The index of refraction of glass is about 1.52. A scientist is observing a plant that is 100.0 cm away from the inside of the glass. To an observer outside the greenhouse, how far does the plant appear to be from the outside of the glass pane?
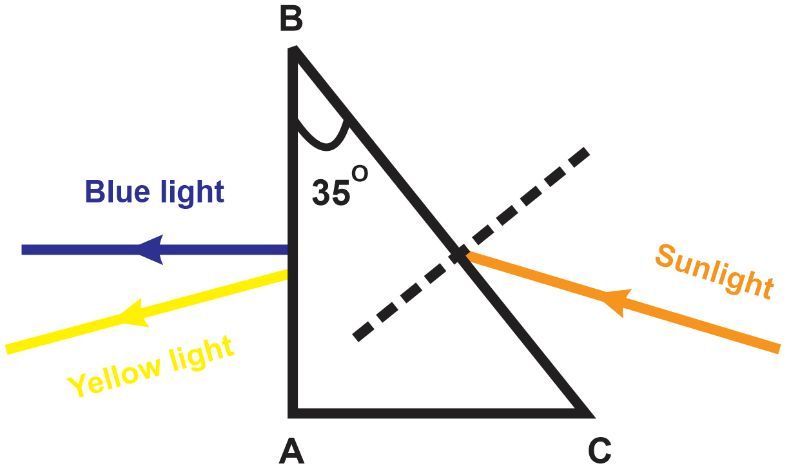
A beam of sunlight strikes a right triangle prism, as shown in the figure below. The incident angle of the beam on side BC of the prism is 60°. The blue light exits side AB parallel to the normal of side AB. Given that the refractive index for yellow in this type of glass is 3.5% higher than that of blue, calculate the angular deviation between the yellow light and the blue light exiting the prism.
A light beam in the air strikes a flat layer of pure quartz of thickness t placed in contact with a thick layer of turpentine oil. The beam is incident on the air-quartz interface at an angle of 28° with respect to the normal to the surface and emerges at angle θr in the turpentine. Determine θr. The refractive indices of quartz and turpentine are 1.54 and 1.47 respectively.
A light ray is incident on a series of two solid slabs, as shown in the figure. The first slab has an index of refraction of 1.53, and the second slab has an index of refraction of 1.47. The light emerges out of the second slab into the air, forming an angle θr with the normal to the surface. Determine θr by exploiting the data given in the figure.