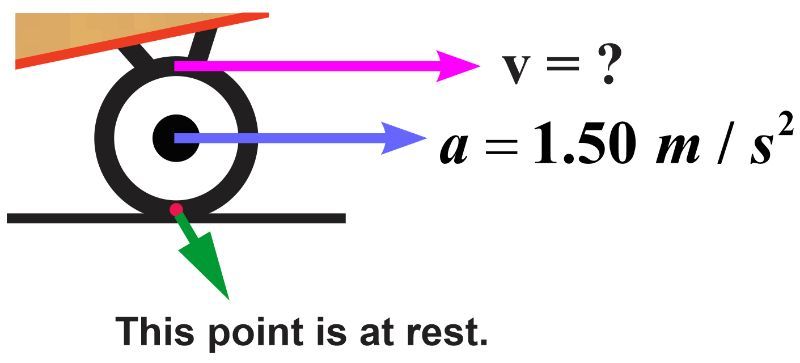- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

A cyclone used for roof ventilation has a diameter of 60.0 cm. Suppose the cyclone has a steady angular acceleration of 0.200 rev/s2. At t= 0, the cyclone has an angular velocity of 0.450 rev/s. At t = 0.800s, determine the tangential speed of a point at the edge of the cyclone.
A circular tabletop has a radius of 1 m. You want to print a spiral decoration whose radius increases outward by spinning the top. The printing head has a constant linear printing speed of 50 mm/s. The decoration starts at an inner radius of 0.10m and ends at an outer radius of 0.90 m. Determine the angular speed of the tabletop when printing the innermost and outermost parts of the decoration.
A thin glass container is placed 7.5 cm from the axis of rotation of a spin coater device. The spin coater rotates at 2500 rpm. Calculate the container's centripetal acceleration.
Shafts are fitted with disks to create useful devices for storing rotational kinetic energy. The disks increase their rotational speeds when extra energy is available and decrease their rotational speeds when required to deliver energy. A shaft fitted with tungsten carbide ceramic bearings spins at 10500 rpm. Calculate the speed at a point located on the edge of a 22 cm diameter disk that is fitted to the rotating shaft.
Determine the speed of a point at the top of a skateboard's wheel that has a diameter of 68.0 cm after 2.76 s has passed, when the skateboarder accelerates from rest at a rate of 1.50 m/s². Please note that the wheel's lowest point remains stationary and in contact with the ground at any moment in time.
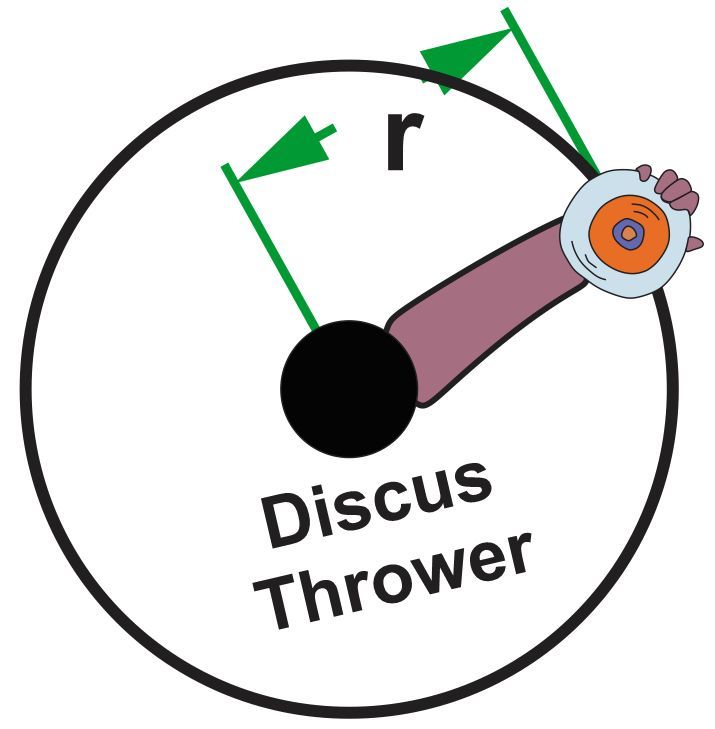
A discus thrower increases the speed of a 2.0 kg discus from zero to 24 m/s while making 2.5 complete rotations. Assuming the angular velocity increases at a constant rate and that the discus moves in a flat circle with a radius of 2.0 meters, determine the tangential acceleration, disregarding air resistance and gravity.
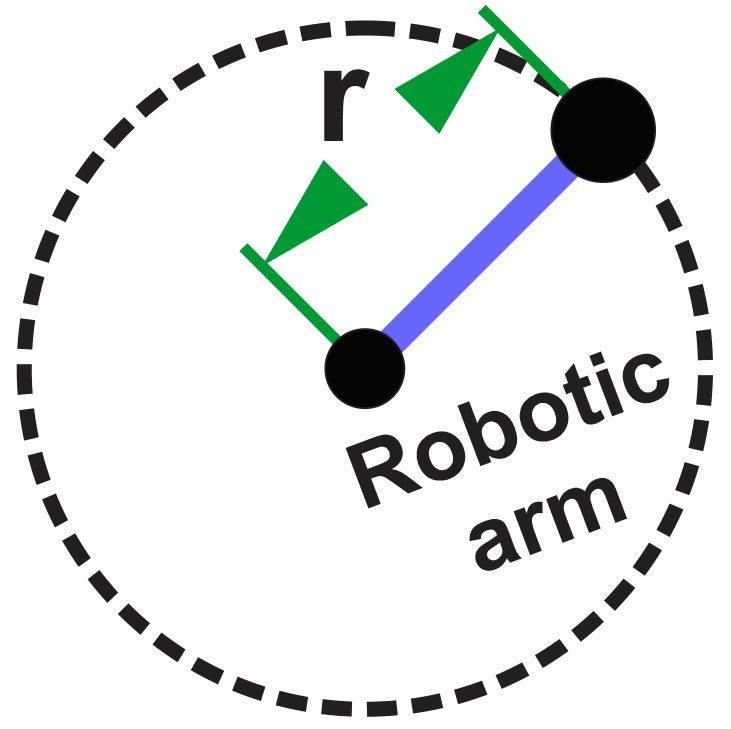
In an automated assembly line, a robotic arm swiftly moves a component of mass 0.50 kg in a circular path with a radius of 0.75 m. The component is accelerated from rest and completes 5.0 full revolutions before being released at a speed of 18.0 m/s onto a designated spot. Assuming the angular acceleration is uniform throughout the motion, calculate the angle of the force exerted by the robotic arm on the component with respect to the radius of the circular path just before release. Ignore the effects of gravity in this scenario.
In a supercomputer's memory disk rotating at 7400 rpm, how many bits can the laser writer store per second if each bit requires 0.60 μm of space and the writer is 5.00 cm from the center?