- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

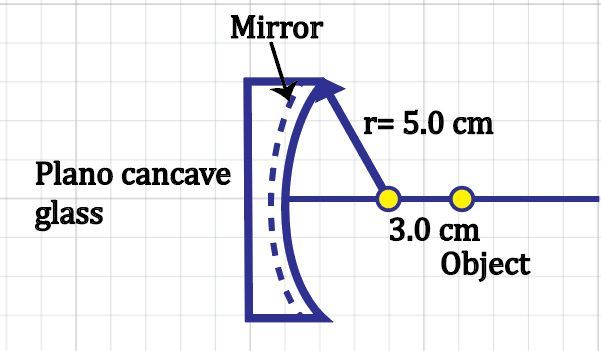
Imagine a mirror is covered with a plano-concave glass, as shown in the figure below. The mirror and the curved surface of the glass both have the same radius of curvature. Consider a sphere, that is modeled like a point object, is placed outside the glass. Determine what the image distance formed by the mirror will be when measured from the mirror's surface.
A grasshopper of height 1.0 cm sits at 14.0 cm on the left side of a concave spherical mirror. The magnitude of the radius of curvature for the mirror is 20.0 cm. Find (i) the position and (ii) the size of the grasshopper image. iii) Specify the characteristics of the image.
A 0.5-mm-tall ant is situated along the principal axis of a thin, spherical shell of quartz coated with aluminum. The ant is 7.0 cm away from the mirror vertex, as shown in the image. The shell has a radius of 8.0 cm. i) Locate and ii) calculate the height of the ant's image.

A turtle lives in a spherical glass tank filled with water that has a radius of 25 cm. The turtle notices a dog sniffing around their tank. The dog's nose is located 10 cm from the tank's outside edge. From the turtle's perspective inside the tank, how far is the dog's nose located from the outside edge of the tank? (Assume that the glass tank's thickness can be ignored.)
A jewelry appraiser uses a large, solid glass sphere with a radius of 9.0 cm. He places a small, intricate diamond 8.0 cm from the sphere's surface. The diamond's image is formed on the opposite side of the glass sphere. Determine the distance between the diamond image and the sphere's center.
A bug is placed 10.0 cm in front of a lens. The lens forms an image on a white screen 30.0 cm behind the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
In an advanced infrared laser system, a plano-concave lens composed of germanium is used. The lens, with its flat side facing the object, produces an image from an infrared source. The magnification of this produced image is +0.40, and the distance from the infrared source to the lens is 50 cm. Given that the refractive index of germanium is 4.01, calculate what the radius of curvature will be for the curved surface of the lens.
A child is playing with a large, perfectly spherical sapphire marble that has a refractive index of n = 1.77 and a diameter of 8.0 cm. She places a small figurine 4.8 cm away from the edge of the marble and notices that an image of the figurine forms on the opposite side of the marble. Consider what would happen if the marble was replaced with a thin lens that is placed where the center of the marble had been located originally and if the image remains in the same position, what would be the lens's focal length in this case?
A science instructor holds her phone 2.0 m away from a whiteboard. The teacher wants to magnify the device's screen three times using a lens. Determine the focal length and distance at which the lens should be positioned (with respect to the phone) to obtain this effect.