- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

A balloon of volume 0.00320 m3 contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1.20 × 105 Pa. The number of moles in the ballon is 0.120. The balloon expands to 1.8 times the original volume. Calculate the final temperature (in K) and pressure assuming an isobaric process.
Consider a sample of helium gas with a mass of 7.0 g, an initial pressure of 2.0 atm and an initial temperature of 25°C. Helium is compressed at constant pressure until its volume is reduced to one-third of its initial value. Determine the final temperature of the gas.
How much heat energy is transferred from a 4.00 g of oxygen gas that initially has a volume of 2.50 liters and a pressure of 4.0 atm, and is then compressed at constant pressure until the volume is reduced by half, and finally undergoes an isochoric process until the gas reaches its original temperature of 25.0°C?
A chef wants to reduce the cooking time by a few minutes. To succeed, he raises the pressure to 4 atm inside the cooker. At this pressure, the boiling point of water, the density of water, and the density of steam are 144 °C, 922.2 kg/m3, and 2.163 kg/m3 respectively. What is the work (W) done by 200 g of steam formed at 144 °C inside the cooker?
During a laboratory experiment, a student uses a piston-cylinder assembly initially containing 10 cm3 of an ideal gas. The cylinder is heated with an electric resistor to maintain constant pressure of the expanding gas. The net energy added to the gas by heat is 5 J and the pressure sensor inside the cylinder indicates a value of 3 × 105 Pa. Find the work done by the gas if the volume of the cylinder is doubled.
A gas enclosed in a piston-container assembly loses 340 J of heat as it is compressed from 450 cm3 to 200 cm3 at constant pressure. The internal energy of the gas increases by 220 J. Calculate the pressure during the process.
0.20 grams of neon is treated through the thermodynamics paths shown below. Calculate the net heat energy that flows into/out of the gas in the three-step process.

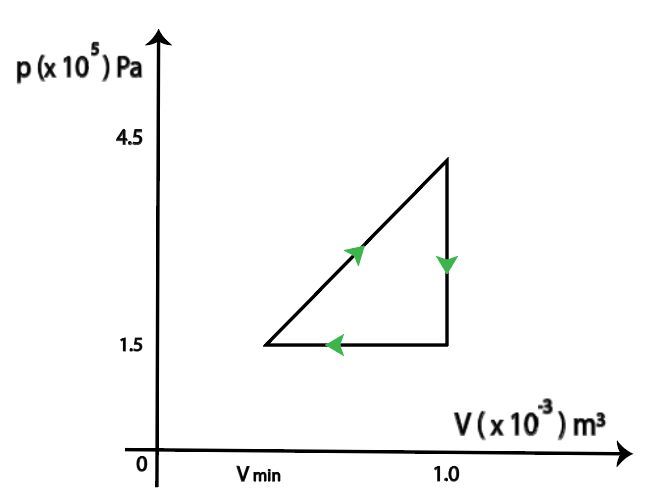
The pV diagram of a cyclic transformation of 1.0 mole of helium gas is shown below. The work produced during the cycle is 80 J. Determine Vmin.
A model of the lungs can be made using a balloon inside a container fitted with a movable piston. The balloon is connected to the atmosphere using a pipe. Air is sucked into the balloon when the piston is lowered and expelled when the piston is raised. An idealized curve with straight lines instead of curves for sucking and expulsion is shown below. Note: The curve is labeled using gauge pressure rather than absolute pressure. Determine the net work done by the ballon in one cycle.

An ideal gas in a container with a piston is taken through a two-step process. In the initial step, volume is kept constant at 0.800 m3 as the pressure is raised from 0.980 × 105 Pa to 4.20 × 105 Pa. In the subsequent step, the gas is compressed, keeping the pressure constant at 4.20 × 105 Pa to a final volume of 0.450 m3. What is the total work done during this two-step process?
A container is filled with 1.8 moles of an ideal gas. The gas is heated from 18°C to 90°C while keeping the pressure constant. Which diagram qualitatively represents the PV diagram for this process?
A gas is compressed and the work done on the gas is -5000 J as illustrated in the diagram below. What is the pressure pa of the gas?

The process shown in the diagram below occurs on a gas. During this process, the gas has 70 J of work performed on it. Determine the value of V in liters.