Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Wave Function
The wave function describes the displacement of a wave at any point in space and time. In the case of standing waves, it can be expressed as a product of two sine functions, representing the spatial and temporal components. Understanding the wave function is crucial for analyzing wave behavior, including amplitude, frequency, and wavelength.
Recommended video:
Wave Speed
Wave speed is the rate at which a wave propagates through a medium, calculated as the product of its frequency and wavelength. For traveling waves, the speed can be determined using the formula v = fλ, where v is wave speed, f is frequency, and λ is wavelength. In the context of standing waves, the wave speed can be derived from the properties of the individual traveling waves that compose it.
Recommended video:
Intro to Waves and Wave Speed
Standing Waves
Standing waves are formed by the interference of two traveling waves moving in opposite directions with the same frequency and amplitude. They are characterized by fixed nodes (points of no displacement) and antinodes (points of maximum displacement). Understanding the formation and properties of standing waves is essential for analyzing their wave functions and determining related parameters such as wave speed.
Recommended video:
Intro to Transverse Standing Waves
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution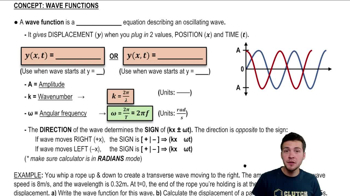



 6:32m
6:32m