Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electric Charge
Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Charges can be positive or negative, with electrons carrying a negative charge. The net charge of an object is the total charge it possesses, which can result from the gain or loss of electrons.
Recommended video:
Excess Electrons
Excess electrons refer to the additional electrons that an object accumulates, resulting in a net negative charge. The number of excess electrons can be calculated by dividing the total charge by the charge of a single electron, which is approximately -1.6 x 10^-19 coulombs. This concept is crucial for understanding how static electricity is generated through friction.
Recommended video:
Electrons In Water (Using Density)
Mass Increase from Charge
When an object accumulates charge, its mass can theoretically increase due to the mass-energy equivalence principle, as described by Einstein's equation E=mc². However, the mass increase from the addition of electrons is extremely small and often negligible in practical scenarios. The increase can be calculated by determining the total energy associated with the excess charge and converting it to mass.
Recommended video:
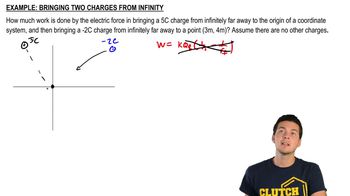
Work to Bring Two Charges From Infinity
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 6:36m
6:36m