Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Pressure
Pressure is defined as the force applied per unit area. In this context, it is crucial to understand how the applied force on the plunger translates into pressure within the fluid system. The gauge pressure, measured in mm-Hg, indicates the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure and is essential for determining the force needed to overcome this pressure to initiate fluid movement.
Recommended video:
Pressure and Atmospheric Pressure
Hydraulic Systems
Hydraulic systems operate on the principle that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid. This concept is vital for understanding how the force applied to the plunger affects the fluid in the needle. The relationship between the areas of the plunger and the needle also plays a significant role in calculating the necessary force to achieve the desired pressure.
Recommended video:
Pascal's Law and Hydraulic Lift
Force and Area Relationship
The relationship between force and area is described by the equation F = P × A, where F is the force, P is the pressure, and A is the area. In this scenario, the area of the plunger and the needle must be calculated to determine the force required to achieve the gauge pressure of 75 mm-Hg. Understanding this relationship is essential for solving the problem effectively.
Recommended video:
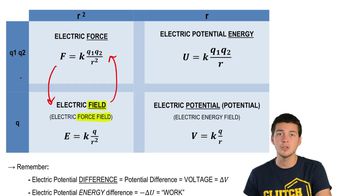
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 17:41m
17:41m