Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Capacitance
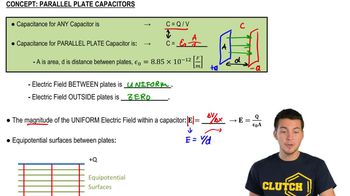
Capacitance is a measure of a capacitor's ability to store charge per unit voltage. It is defined as C = Q/V, where C is capacitance, Q is the charge stored, and V is the voltage across the plates. For parallel-plate capacitors, capacitance can also be calculated using the formula C = ε₀(A/d), where ε₀ is the permittivity of free space, A is the area of one plate, and d is the separation between the plates.
Recommended video:
Capacitors & Capacitance (Intro)
Electric Field
The electric field (E) in a capacitor is the force per unit charge experienced by a positive test charge placed in the field. It is uniform between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor and is given by E = V/d, where V is the voltage and d is the distance between the plates. The strength of the electric field is crucial for determining the potential difference and the charge on the plates.
Recommended video:
Charge on Plates
The charge (Q) on each plate of a capacitor can be calculated using the relationship Q = C × V. Once the capacitance is determined from the physical dimensions and the electric field strength, and the voltage is derived from the electric field and plate separation, the total charge can be computed. This charge is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign on the two plates, leading to the storage of electrical energy in the capacitor.
Recommended video:
Parallel Plate Capacitors
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 3:43m
3:43m