Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electrostatic Charge
Electrostatic charge refers to the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Objects can be positively charged, negatively charged, or neutral, depending on the balance of protons and electrons. When a charged object comes into contact with a neutral object, it can transfer charge, leading to the phenomenon of attraction or repulsion between the objects.
Recommended video:
Electroscope Functionality
An electroscope is a device used to detect electric charge. It consists of a metal rod connected to two thin metal leaves. When the electroscope is charged, the leaves acquire the same type of charge, causing them to repel each other due to the electrostatic force. This repulsion is a clear indicator of the presence of charge in the electroscope.
Recommended video:
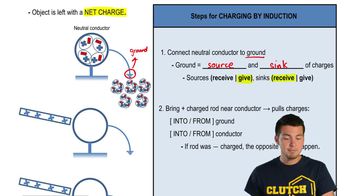
Charge Induction
Charge induction is the process by which a charged object can cause a redistribution of charges in a nearby neutral object without direct contact. When a positively charged glass rod is brought near the electroscope, it attracts electrons from the leaves, causing them to become negatively charged. This results in both leaves having the same negative charge, leading to their repulsion from each other.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 6:36m
6:36m