Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Position-Time Graph
A position-time graph illustrates the position of an object over time. The slope of the graph at any point indicates the object's velocity. A horizontal line indicates zero velocity, while a positive slope indicates positive velocity and a negative slope indicates negative velocity. Understanding how to interpret these slopes is crucial for analyzing motion.
Recommended video:
Curved Position-Time Graphs & Acceleration
Velocity
Velocity is the rate of change of position with respect to time and is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. It can be calculated as the change in position divided by the change in time. In the context of the graph, points where the slope is zero correspond to times when the velocity is zero, while the steepness and direction of the slope indicate when the velocity is most positive or negative.
Recommended video:
Oscillatory Motion
Oscillatory motion refers to the repetitive back-and-forth movement of an object around an equilibrium position, such as a block attached to a spring. This motion can be analyzed using position-time graphs, where the periodic nature of the graph reflects the oscillations. Understanding oscillatory motion helps in predicting the behavior of the block as it moves up and down after being released.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution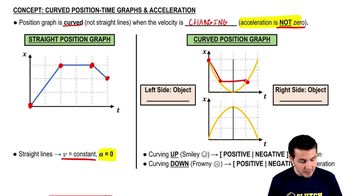



 9:48m
9:48m