Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy (U) is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field. It is defined relative to a reference point, typically where the potential energy is considered zero, such as when objects are infinitely far apart. For a mass m at a distance x from a mass distribution, U can be calculated by integrating the gravitational force over the distance. Understanding this concept is crucial for solving problems involving gravitational interactions.
Recommended video:
Gravitational Potential Energy
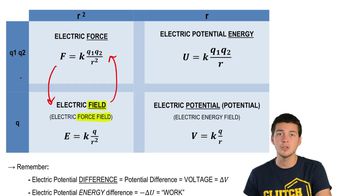
Force and Potential Energy Relationship
The relationship between force (F) and potential energy (U) is given by the equation F = -dU/dx, which indicates that the force acting on an object is the negative gradient of the potential energy with respect to position. This means that the force points in the direction of decreasing potential energy. This concept is essential for determining the force acting on the particle in the given problem, as it allows us to derive the force from the potential energy function.
Recommended video:
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Limitations and Approximations in Physics
In physics, approximations are often used to simplify complex problems. In this context, when the distance x is much larger than the radius a of the ring, the gravitational effects can be approximated as if the mass were concentrated at a point. This simplification allows for easier calculations and helps verify that the derived expressions for potential energy and force align with expected results in classical mechanics, reinforcing the validity of the models used.
Recommended video: