Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Vector Cross Product
The vector cross product is a mathematical operation that takes two vectors and produces a third vector that is perpendicular to the plane formed by the original vectors. The direction of the resulting vector is determined by the right-hand rule, which states that if you curl the fingers of your right hand from the first vector to the second, your thumb points in the direction of the cross product.
Recommended video:
Vector (Cross) Product and the Right-Hand-Rule
Right-Hand Rule
The right-hand rule is a mnemonic used to determine the direction of the cross product of two vectors. To apply it, extend your right hand with your fingers pointing in the direction of the first vector and curl them towards the second vector. Your thumb will then point in the direction of the resulting vector from the cross product.
Recommended video:
Force on Moving Charges & Right Hand Rule
Magnitude of Cross Product
The magnitude of the cross product of two vectors is calculated using the formula |A x B| = |A| |B| sin(θ), where |A| and |B| are the magnitudes of the vectors and θ is the angle between them. In the case of perpendicular vectors, the sine of 90 degrees is 1, making the magnitude equal to the product of the magnitudes of the two vectors.
Recommended video:
Vector (Cross) Product and the Right-Hand-Rule
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution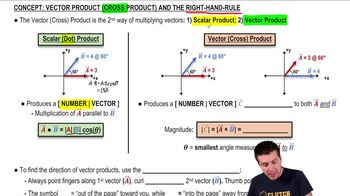



 1:30m
1:30m