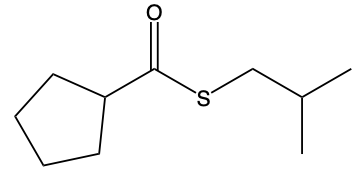
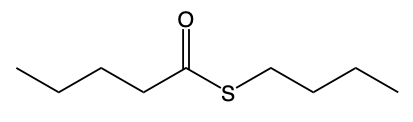
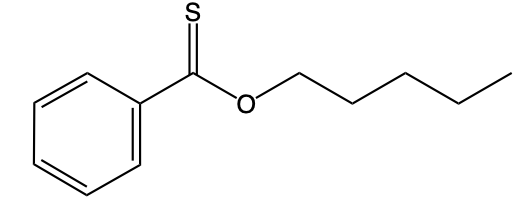
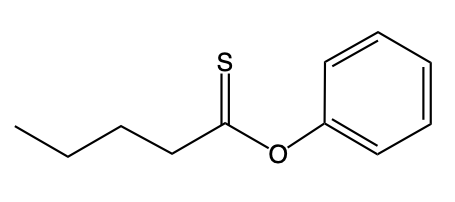
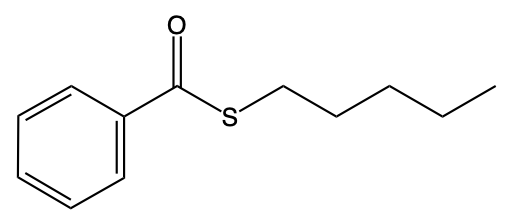
Hey, everyone. So let's take a look at the introduction to thioesters. Now we're going to say thioesters themselves are sulfur analogs of esters. And we're going to say there are two types of them. We have our s alkyl thioester, which is the common one.
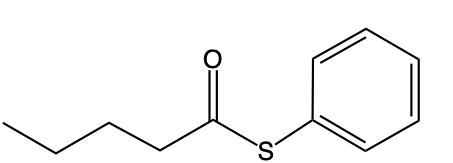
If we take a look at the image to the right, we're going to say this represents an s alkyl thioester. As we can see, it has a carbonyl group. This carbonyl group is connected to a sulfur, which in turn is connected to an r group. In this case, this r group represents a carbon group. Then we have our O alkyl thioester, which would be this one.
Notice the differences. Now we no longer have our typical carbonyl group where it is carbon double bonded to oxygen. Instead, we have carbon double bonded to sulfur. Then that carbon is single bonded to an oxygen, which in turn is single bonded to an r group and an alkyl group. Now we're going to say here that these s thioesters, which again are the first image, are also known as thioesters.
So just remember, when we're talking about these thioesters, they can either be in the form of an s alkyl thioester, or they can be in the form of an o alkyl thioester. The first one is the more common version of these two possibilities.