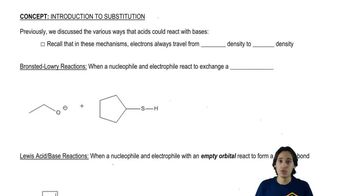
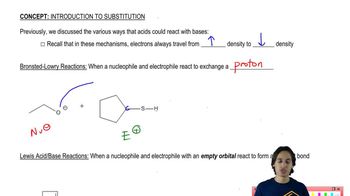
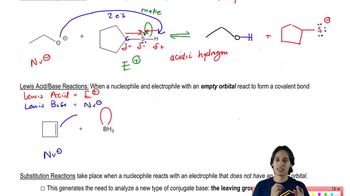
7. Substitution Reactions
Nucleophilic Substitution
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceGiven the curved arrow formalism, predict the products of the following reaction:394views
- Multiple ChoiceBased on the curved arrow formalism given, predict the products of this acid/base reaction.487views
- Textbook Question
In contrast to the results of Assessment 13.18, when a secondary haloalkane is treated with sodium ethanethiolate, we predict formation of a thioether. How is this rationalized?
433views - Textbook Question
Predict the product of the following substitution/addition reactions involving phenoxides. [Because this problem represents a review of current and previous material, section numbers have been provided for your reference.]
(d)
488views - Textbook Question
The reaction of an alkyl chloride with potassium iodide is generally carried out in acetone to maximize the amount of alkyl iodide that is formed. Why does the solvent increase the yield of alkyl iodide?
(Hint: Potassium iodide is soluble in acetone, but potassium chloride is not.)
448views - Textbook Question
The following functional-group interchange is a useful synthesis of aldehydes.
(c) Explain why a nucleophilic reagent such as ethoxide adds to an alkyne more easily than it adds to an alkene.
379views - Multiple ChoiceWhich type of nucleophilic substitution reaction is most likely to occur when pyrimidine dimers in DNA are repaired, potentially leading to mutations that can cause cancer?66views