- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

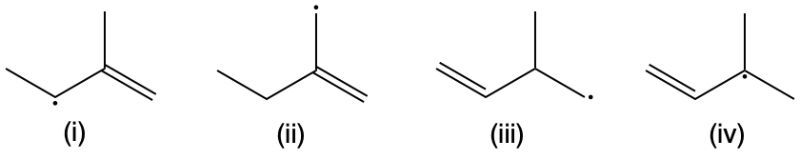
Rank the following reactive intermediates in order of decreasing reactivity:
Rationalize the ranking of the following ethers according to their ability to form explosive peroxides.

Considering the relative stabilities of the resulting alkyl radicals, determine which of the indicated carbon-hydrogen bonds would have a higher value of the bond dissociation energy.

Determine which of the following radicals is the most stable, and thus, is most likely to be produced from an ether.

A graduate student was studying free radical halogenation reactions. She added NBS to a solution of 3-methylcyclopent-1-ene and irradiated the mixture with a sunlight lamp. After all of the added NBS was consumed, she found that the reaction resulted in four different isomeric products of the formula C6H9Br. Rank the four allylic radicals that produce the four isomeric products.
The following three alkenes are arranged in decreasing order of their bond rotational energy barriers. Consider their transition states to explain the difference in bond rotation energies.

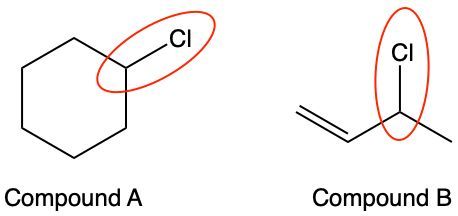
Considering the stability of the generated radicals, does the encircled bond in compound A have a higher bond-dissociation energy than the encircled bond in compound B?