- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

What is the name of the following compound?

Some protecting groups can protect two hydroxy groups on a carbohydrate at the same time. One such group protects the OH groups at carbon 4 and carbon 6 of β-D-mannose, as shown below.

a. To what functional group does this protecting group belong?
b. What reagent is employed in the synthesis of such protected compounds?
c. When this blocking group is coupled with β-D-mannose, a new chiral center is formed. What is its location?
d. Draw the compound's other stereoisomer and assess which stereoisomer should be more stable.
Tetraisopropyldisiloxanyl, or TIPDS, is an important protective group created specifically for polyhydroxy substances like sugar. TIPDS can shield two alcohol groups of a molecule:

a. The isopropyl groups around the Si atoms hinder the TIPDS group slightly. Which —OH of 1-methoxy-α-D-arabinofuranose has a higher chance of reacting with TIPDS chlorine first? Draw the product with one oxygen attached to the TIPDS group.
b. Once the TIPDS group has been connected to the first oxygen, the next oxygen nearest to it is reached. Draw the final product with TIPDS attached to two oxygens.
c. Now that the oxygens are shielded, the unprotected hydroxy group can undergo a reaction. Draw the final product formed when treating the protected 1-methoxy-α-D-arabinofuranose from (b) with tosyl chloride, pyridine, and NaBr.
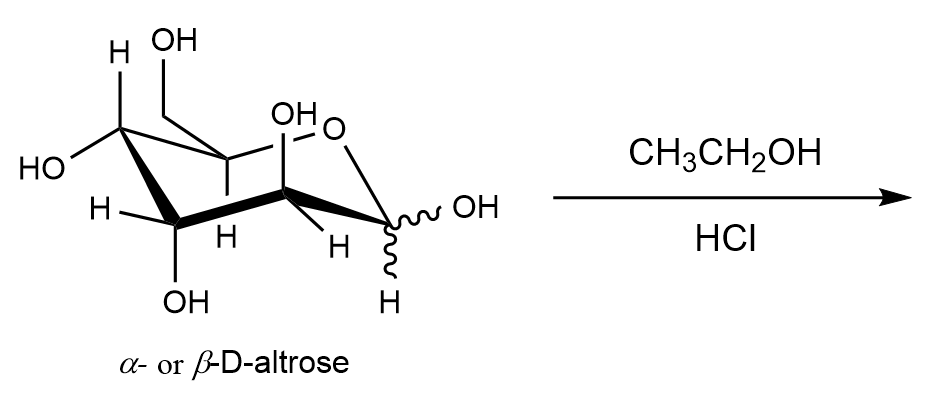
Draw the product(s) obtained in the reaction of D-altrose with ethanol and HCl.