- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Provide the stereoisomer that would be obtained in the greatest yield when 4-chloro-3-ethyl-4-methylheptane reacts via the E2 mechanism.
Give the identity of products obtained in each elimination reaction shown below.
Determine which is the major product if more than one type of product can be obtained in the reactions.
Also provide a brief explanation for your answers by comparing the degree of substitution of each double bond in the products.
(i) 2-bromohexane + NaOCH3 →
(ii) 3-chloro-3-methylpentane + NaOCH3 →
(iii) 2-chloro-3-methylpentane + NaOH →
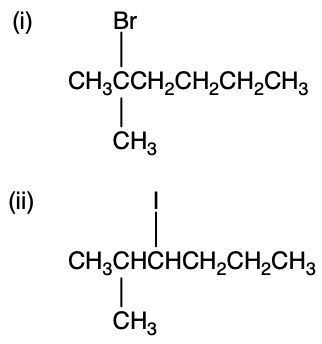
Determine the major elimination products generated when the alkyl halides below react with hydroxide.
Considering the heat of hydrogenation, determine whether cyclohexa-1,4-diene or cyclohexa-1,3-diene is more stable.

When one equivalent of Br2 reacts with 2,3-dimethylbuta-1,3-diene, two alkene products are formed. Determine which alkene is more stable. Why?

Rank the following substances in order of increasing stability.
cis-5-decene; (Z)-3,6-diethyloct-4-ene; (Z)-5,6-dimethyldec-5-ene; trans-5-decene
Show the products of the dehydrohalogenation reactions of the following alkyl halides using potassium hydroxide. Also, label these products as major and minor.
The double elimination of H―Cl from a dihaloalkane under basic conditions is an alternative method to synthesize alkynes. Suggest a mechanism for this reaction.

Show how the following synthetic transformation can be accomplished. Give the structures of all intermediates.
2,2-dibromopentane → pent-2-yne
Which acetylide ion and carbonyl can be used to synthesize 3,7-dimethyloct-4-yn-3-ol?
Draw a suitable mechanism for the acetylide alkylation reaction given below.