- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Provide the Haworth projections of the furanose rings of the compound below.

Show the structures of the sugar derivatives given below.
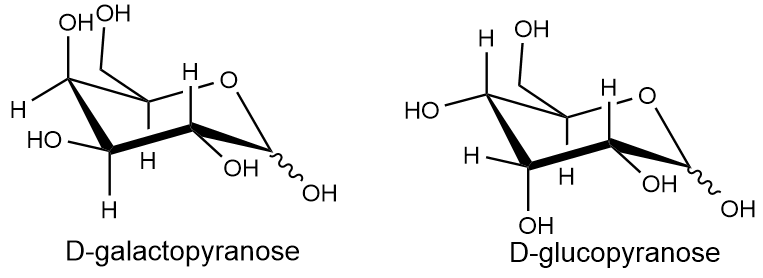
4-O-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-D-galactopyranose
Lactose is a sugar molecule made up of two subunits: D-glucopyranose and D-galactopyranose. These subunits are connected by a β-1,4′-glycosidic linkage. In an experiment, lactose was treated with two chemical processes: first with methyl iodide (CH3I) in excess with silver oxide (Ag2O), then with HCl/H2O. After these treatments, it was observed that the D-galactopyranose part had only one hydroxyl (OH) group that wasn't converted to a methoxy group, while the D-glucopyranose part had two such groups. Draw the structure of α-lactose based on this information.
For the disaccharide below: (i) determine its reducing end, (ii) specify the monosaccharides that constitute it, and (iii) describe the type of its glycosidic bond.
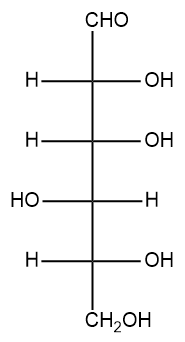
Provide the structures of the α- and β-anomers of D-gulopyranose. The Fischer projection for D-gulose is shown below.
Draw the structure(s) of the cyclic hemiacetal formed by the 5-hydroxyaldehyde, 5-hydroxyhexanal.
Provide the structure(s) of the cyclic hemiacetal formed by the 4-hydroxyaldehyde, 4-hydroxy-5-methylhexanal.
Which structure shows the five-membered ring lactone formed from the aldaric acid of D-mannose?
Glucose undergoes mutarotation in an aqueous solution. The specific rotation of pure α-D-glucose is +112.2° and pure β-D-glucose is +18.7°. When the pure α or β anomer is dissolved in water, it mutarotates and the specific rotation changes to +52.6°. Using the specific rotation values, calculate the percent of each anomer present in the solution at equilibrium.
A scientist wants to determine the percentage of α-D-mannose and β-D-mannose in an equilibrium solution. The specific rotation of α-D-mannose is +20.3°, while that of β-D-mannose is −17.0°. At equilibrium, the specific rotation is +14.2°. What are the percentages at equilibrium?
When lactose hydrolyzes, a mixture of galactose and glucose with a ratio of 1:1 has a specific rotation of +134.7°. What is the specific rotation of an equilibrium mixture of galactose? [Note: The specific rotation of glucose at equilibrium is +52.7°.]
Propose a mechanism for the conversion of α-D-galactopyranose to β-D-galactopyranose in an acidic environment.