- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

The compound below contains alternating double bonds and has 14 π electrons (4n + 2 with n = 3), therefore, it is aromatic. Is this statement true or false? Explain.
Identify each of the structures shown below as nonaromatic, antiaromatic, or aromatic. Provide a brief explanation for your answer.

Which of these heterocyclic compounds are aromatic? Explain your answer briefly.
Classify each of the following compounds as nonaromatic, antiaromatic, or aromatic. Provide a brief explanation for your answer.

Identify the following heterocyclic compounds as aromatic or nonaromatic.

Provide the Frost diagram for the given ion. Determine whether it is aromatic or antiaromatic.

Illustrate the Frost circles for the cycloheptatrienyl anion and cycloheptatrienyl cation. Differentiate the two.
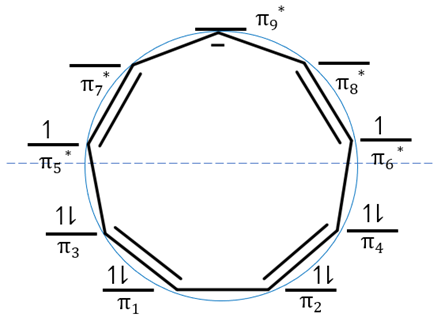
The Frost circle was used to draw the molecular orbital energy diagram of cyclononatetraenyl anion. Using this diagram, it was determined that cyclononatetraenyl anion is antiaromatic. Is this correct? Justify your answer.
Why is indene a stronger acid than indole even though the electronegativity of nitrogen is greater than that of carbon?

Suggest the relative pKa values of the following compounds.

Explain why the double-bonded nitrogen in indazole accepts a proton more readily than the other nitrogen.

Determine if each nitrogen atom in the following heterocycle compounds is weakly or strongly basic based on the availability of its non-bonding electron pair.