- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

How can the following compounds be differentiated using IR spectroscopy?

Determine how IR spectroscopy can be used to confirm that the following reaction has been completed. Also, how could you confirm that all of the NH2—NH2 was removed after purification?

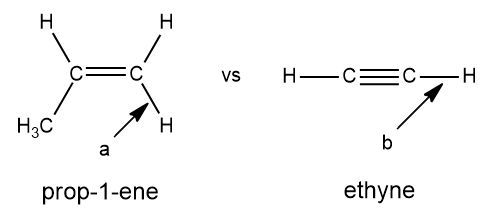
Will bond b of ethyne absorb at a higher or lower wavenumber than bond a of prop-1-ene? Briefly explain.
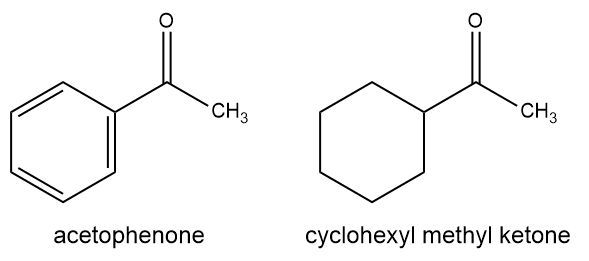
We know that when substituents are properly positioned, they can transmit electronic information through the benzene ring. This concept can be discovered and applied using IR spectroscopy. Would you expect the carbonyl stretching band to appear at a higher frequency for cyclohexyl methyl ketone or acetophenone? Explain.
When placed correctly, substituents can transmit electronic information through the benzene ring. This concept can be discovered and applied using infrared spectroscopy. Explain the carbonyl stretching frequencies for 4-chloroacetophenone and 4-fluoroacetophenone.

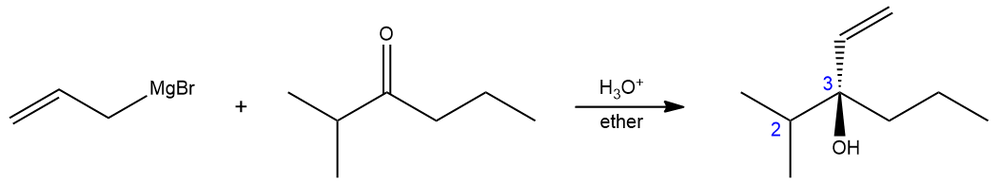
In an organic chemistry lab experiment, 2-methyl-3-hexanone is reacted with allyl magnesium bromide yielding a tertiary alcohol. The 1H NMR of 2-methyl-3-hexanone shows that the two methyl groups are equivalent indicated by one doublet peak. On the other hand, the product (a racemic mixture), gives two different 3H doublets.
(i) Along the C2–C3 axis, show the Newman projection of the product.
(ii) Why do the methyl groups of the product show different signals? What is the term used to describe such groups?
Consider the following compounds. Identify the compound with enantiotopic hydrogens marked by Ha and Hb.

In the given molecule, explain why the hydrogens H a and Hb are nonequivalent.

What is the relationship between the two products obtained when we replace H a and Hb of propane-2-thione with deuterium? How many signals would you expect for these hydrogens in the 1H NMR spectrum?

Sketch the signal for an octet and provide the ratio of its peaks.
Determine the 1H NMR splitting pattern of the marked hydrogens in the given compound.

Determine the number of sets of equivalent protons present in the following molecule.

Determine the expected number of signals in the 1H NMR spectrum for each structural isomer of C5H12.