- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

We often repeat the same steps when performing synthetic analysis to produce the desired product. To see this in action, use the alkynide synthesis to determine how the following aldehyde is produced, starting with an organic molecule with three or fewer carbons.

Using but-1-ene as your starting material, show how the following compounds can be synthesized.
(i) propanoic acid
(ii) propanal
(iii) hept-4-yn-3-ol
Provide the missing products in each step of the given synthesis and show any important stereochemistry.

How could the molecule shown below be synthesized using 2,3-dimethylbut-1-ene as the initial molecule?

Show how you would convert the starting alcohol into the product below.

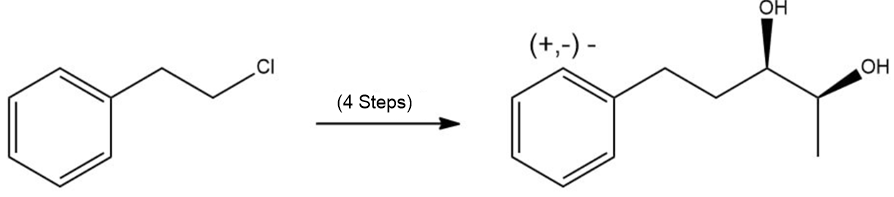
Propose a synthesis of the compound on the right starting with the structure on the left. Although other synthetic routes are possible, the ideal number of steps is shown above the reaction arrow.
Write a possible reaction sequence to synthesize the following aldehyde from the given alkyl halide.

Describe the steps required to make hexan-3-ol using but-1-yne, any inorganic reagents, and any organic molecule with less than four carbons.
Show how you would synthesize each of the following compounds using cyclopentane as your starting material.
(a) bromocyclopentane
(b) cyclopentene
(c) ethoxycyclopentane
Show how you would synthesize each of the following compounds using cyclopentane as your starting material.
(a) 3-bromocyclopent-1-ene
(b) cyclopenta-1,3-diene
(c) cyclopentanol