- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Using the formal charge as a reference, find out the number of unpaired or non-bonding electrons on the marked atom.

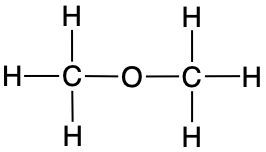
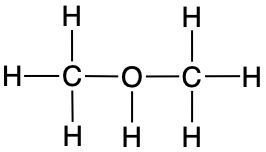
Add the missing lone-pair electrons and formal charges to complete the structures of the compounds shown below:
i.
ii.
Consider the line-angle structure shown below:

(1) Identify the total number of carbon atoms.
(2) Label each carbon (use a through l).
(3) Determine the number of hydrogens at each carbon atom.
(4) Provide the condensed structural formula.
How many hydrogen atoms are bonded to each indicated carbon in the structure of the morphine derivative shown below?

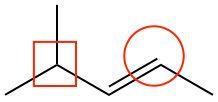
Consider the following line-angle drawing:
(i) Determine the number of carbons in the molecule.
(ii) Determine the number of hydrogens of the encircled carbon.
(iii) Determine if the boxed carbon is 1°, 2°, 3°, or 4°.
Write the appropriate Lewis structures for these free radicals ・CH3 and ・CH(CH3)2.
Draw Lewis structures with the appropriate formal charges for these compounds and ions (CH3)2O—BCl3, H3CNH3+, NaOC(CH3)3, and (CH3)2C=OH+.
Draw Lewis structures for the following molecular formulas: C2H4 (one double bond), C4H6 (two double bonds), and C4H6 (one triple bond). Mark all non-bonding electrons in each structure.
Draw a skeletal structure corresponding to each of the following condensed structures.
a. CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH2CH(CH3)2
b. (CH3)3COC(CH3)3
c. (CH3)2CHOH
Provide the skeletal structure for CH3CH2CH2COOH.
What are the condensed structures of the following compounds drawn as models?
(black = C, white = H, red = O, green = Cl)
Consider the formula, C12H18O2BrF. Provide the index of hydrogen deficiency of the compound.
Determine the IHD for the following molecule.