Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the spatial arrangement of atoms in molecules. It is crucial for understanding isomerism, where compounds with the same molecular formula can have different structures and properties. In organic chemistry, stereochemistry helps determine the configuration of chiral centers, which is essential for identifying whether a compound is designated as 'd' (dextrorotatory) or 'l' (levorotatory).
Recommended video:
Polymer Stereochemistry Concept 1
Chirality
Chirality refers to the property of a molecule that makes it non-superimposable on its mirror image, much like left and right hands. Chiral molecules often contain one or more carbon atoms bonded to four different substituents, creating two distinct enantiomers. The designation of 'd' or 'l' relates to the optical activity of these enantiomers, which is determined by their interaction with plane-polarized light.
Recommended video:
Optical Activity
Optical activity is the ability of a chiral compound to rotate the plane of polarized light. This property is measured using a polarimeter, and the direction of rotation indicates whether the compound is 'd' (right-handed) or 'l' (left-handed). Understanding optical activity is essential for distinguishing between enantiomers and determining their specific configurations in organic compounds.
Recommended video:
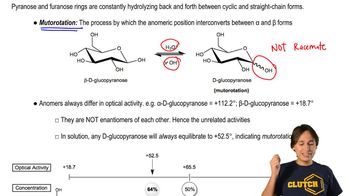
Mutorotation and Optical Activity