Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons consisting only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms, connected by single bonds. They follow the general formula CnH2n+2, where n is the number of carbon atoms. Alkanes can be straight-chain or branched, and their properties vary with molecular size, influencing boiling points and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Bicyclic Compounds
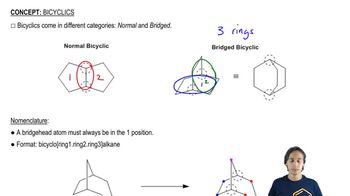
Bicyclic compounds are organic molecules that contain two interconnected rings. In the case of bicyclononane, it consists of nine carbon atoms arranged in a structure that forms two rings. Understanding the connectivity and arrangement of atoms in bicyclic structures is crucial for drawing and naming these compounds accurately.
Recommended video:
The two types of bicyclic molecules
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
The nomenclature of organic compounds follows specific rules set by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). For bicyclic compounds, the naming involves identifying the number of carbon atoms in the rings and the overall structure. Proper naming is essential for clear communication in organic chemistry, especially when multiple structures can fit a given description.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution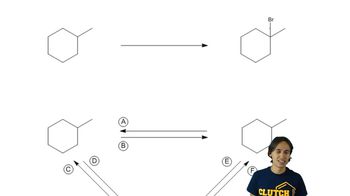


 1:55m
1:55m