Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Formaldehyde as a Carbon Source
Formaldehyde (HCHO) is the simplest aldehyde and serves as a versatile carbon source in organic synthesis. It can participate in various reactions, such as nucleophilic additions, where nucleophiles attack the carbonyl carbon, leading to the formation of alcohols. Understanding how to manipulate formaldehyde in synthetic pathways is crucial for constructing more complex molecules.
Recommended video:
Carbonation of Grignard Reagents
Alkyl Halides in Synthesis
Alkyl halides are organic compounds containing a carbon-halogen bond, which can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions. They are important intermediates in organic synthesis, allowing for the introduction of various functional groups. Recognizing how to use alkyl halides in conjunction with formaldehyde is essential for building the desired alcohol structure in the synthesis process.
Recommended video:
How to name alkyl halides
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
Nucleophilic addition reactions involve the attack of a nucleophile on an electrophilic carbon atom, such as the carbonyl carbon in aldehydes and ketones. This reaction is fundamental in organic chemistry for forming alcohols from carbonyl compounds. Mastery of this concept is vital for designing synthetic routes that convert formaldehyde and alkyl halides into the target alcohol.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution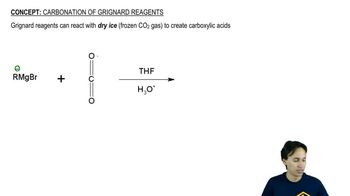



 2:26m
2:26m