Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Aniline Structure and Reactivity
Aniline is an aromatic amine with the formula C6H5NH2. Its amino group (-NH2) is a strong activating group for electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, making the benzene ring more reactive towards electrophiles. Understanding the structure and reactivity of aniline is crucial for planning its transformation into more complex aromatic compounds.
Recommended video:
Protection of Aniline Derivatives
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
Electrophilic aromatic substitution is a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry where an electrophile replaces a hydrogen atom on an aromatic ring. This reaction is key to modifying the benzene ring of aniline to introduce additional substituents, such as methyl groups, which are necessary for synthesizing 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene. Familiarity with EAS mechanisms and regioselectivity is essential for this conversion.
Recommended video:
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
Friedel-Crafts alkylation is a specific type of electrophilic aromatic substitution that involves the introduction of alkyl groups onto an aromatic ring using alkyl halides and a Lewis acid catalyst. This reaction is particularly useful for converting aniline into 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene by sequentially adding methyl groups to the benzene ring. Understanding the conditions and limitations of this reaction is vital for successful synthesis.
Recommended video:
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution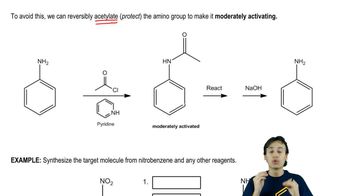



 0:43m
0:43m