Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Tautomerization
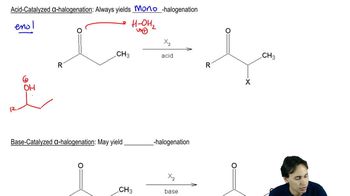
Tautomerization is a chemical reaction that involves the rearrangement of atoms in a molecule, typically involving the transfer of a proton and a shift of a double bond. In this case, the reaction converts a ketone into an alcohol through the formation of an enol intermediate. This process is crucial in organic chemistry as it can influence the reactivity and stability of compounds.
Recommended video:
Tautomerization Mechanisms
Acid-Catalyzed Reactions
Acid-catalyzed reactions involve the use of an acid, such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4), to facilitate the conversion of reactants into products. The acid donates protons, which can stabilize intermediates and enhance the reaction rate. In the provided reaction, H2SO4 acts as a catalyst to promote the tautomerization of the ketone to the corresponding alcohol.
Recommended video:
Mechanism of Tautomerization
The mechanism of tautomerization typically involves the formation of an enol intermediate, where a hydrogen atom is transferred from the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group to the oxygen of the carbonyl. This results in the formation of a double bond between the carbon and the oxygen, followed by protonation and rearrangement to yield the final alcohol product. Understanding this mechanism is essential for predicting the outcome of the reaction.
Recommended video:
Tautomerization Mechanisms

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution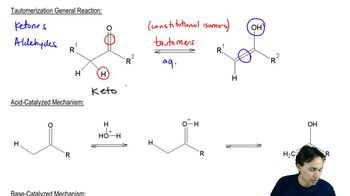


 1:51m
1:51m