Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Proton-Coupled 13C NMR Spectroscopy
Proton-coupled 13C NMR spectroscopy is a technique that provides information about the carbon environment in organic compounds by observing how carbon signals are influenced by nearby protons. In this method, the coupling between protons and carbon atoms leads to splitting patterns in the NMR signals, which can reveal the number of protons attached to each carbon and their spatial arrangement.
Recommended video:
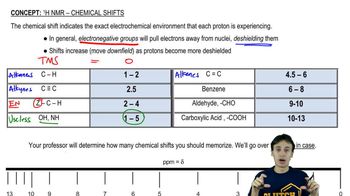
Chemical Shift
Chemical shift in NMR spectroscopy refers to the position of a signal in the spectrum, which is influenced by the electronic environment surrounding the nucleus. In 13C NMR, different functional groups and hybridization states of carbon atoms result in distinct chemical shifts, allowing chemists to deduce structural information about the compound being analyzed.
Recommended video:
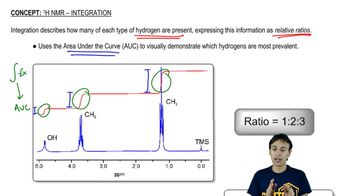
Signal Integration and Multiplicity
Signal integration and multiplicity in NMR provide insights into the number of equivalent nuclei and their interactions. In proton-coupled 13C NMR, the multiplicity of a carbon signal indicates how many protons are directly attached to that carbon, while integration can help quantify the relative number of protons contributing to each signal, aiding in the interpretation of the compound's structure.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 4:m
4:m