Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
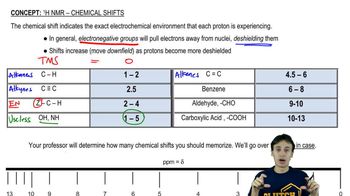
Chemical Shift
Chemical shift refers to the change in the resonant frequency of a nucleus in a magnetic field, which is influenced by the electronic environment surrounding that nucleus. In NMR spectroscopy, it is measured in parts per million (ppm) and provides insight into the chemical environment of protons in a molecule. For proton Hc in styrene, the chemical shift will indicate its position relative to other protons in the molecule.
Recommended video:
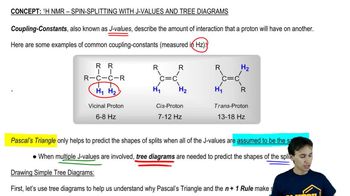
Splitting Tree
A splitting tree is a visual representation used in NMR spectroscopy to illustrate the multiplicity of signals due to spin-spin coupling between neighboring protons. Each branch of the tree represents a different possible state of the protons, helping to predict the number of peaks and their relative intensities in the NMR spectrum. For proton Hc in styrene, the splitting pattern will depend on the number of adjacent protons and their coupling constants.
Recommended video:
Splitting with J-Values:Simple Tree Diagram
Proton NMR Spectroscopy
Proton NMR spectroscopy is a technique used to determine the structure of organic compounds by analyzing the magnetic properties of hydrogen nuclei (protons). It provides information about the number of protons, their chemical environment, and their interactions with neighboring protons. Understanding the principles of proton NMR is essential for interpreting the splitting patterns and chemical shifts of protons, such as Hc in styrene.
Recommended video: