Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Tautomerism
Tautomerism is a chemical phenomenon where two or more structural isomers, known as tautomers, readily interconvert. In the case of 2,4-pentanedione, the keto form and the enol form are tautomers. The stability of these forms can vary significantly depending on the solvent and environmental conditions, influencing the equilibrium between them.
Recommended video:
Tautomerization Mechanisms
Solvent Effects on Tautomerism
The solvent plays a crucial role in determining the stability of tautomers. In non-polar solvents like hexane, the enol form of 2,4-pentanedione is favored due to lower steric hindrance and less solvation of the polar keto form. Conversely, in polar solvents like water, the keto form is stabilized through hydrogen bonding and solvation, leading to a lower percentage of the enol form.
Recommended video:
Tautomerization Mechanisms
Keto-Enol Equilibrium
Keto-enol equilibrium refers to the balance between the keto and enol forms of a compound. Factors such as temperature, solvent polarity, and intramolecular hydrogen bonding can shift this equilibrium. In the case of 2,4-pentanedione, the high percentage of enol in hexane suggests that the non-polar environment favors the enol form, while the significant drop in water indicates that the keto form is more stable in polar conditions.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution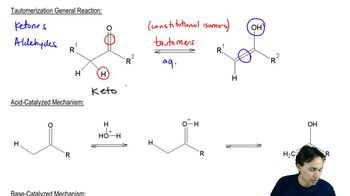



 4:48m
4:48m