Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Keto-Enol Tautomerism
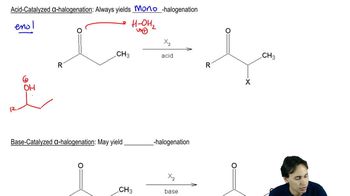
Keto-enol tautomerism is a chemical equilibrium between a keto form (a carbonyl compound) and its corresponding enol form (an alcohol with a double bond). In this process, the hydrogen atom shifts from the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl to the oxygen, resulting in the formation of the enol. This concept is crucial for understanding how cyclopentanone can interconvert between its keto and enol forms under acidic conditions.
Recommended video:
Tautomerization Mechanisms
Acid-Catalyzed Reaction
An acid-catalyzed reaction involves the use of an acid to increase the rate of a chemical reaction. In the context of keto-enol interconversion, the acid protonates the carbonyl oxygen, making the carbonyl carbon more electrophilic and facilitating the transfer of the hydrogen atom to form the enol. This mechanism highlights the role of acids in stabilizing intermediates and promoting reaction pathways.
Recommended video:
Cyclopentanone Structure
Cyclopentanone is a cyclic ketone with a five-membered ring containing a carbonyl group. Its structure influences the stability of the keto and enol forms, as steric and electronic factors can affect the equilibrium between these tautomers. Understanding the molecular structure of cyclopentanone is essential for predicting the outcome of the acid-catalyzed keto-enol interconversion and the relative amounts of each tautomer.
Recommended video:
Drawing Resonance Structures
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution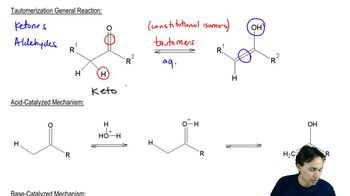


 1:51m
1:51m