Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry is the study of the spatial arrangement of atoms in molecules and how this affects their chemical behavior. It includes concepts such as chirality, where molecules can exist as non-superimposable mirror images (enantiomers), and diastereomers, which are stereoisomers that are not mirror images. Understanding stereochemistry is crucial for analyzing the configurations of compounds like tartaric acid and its derivatives.
Recommended video:
Polymer Stereochemistry Concept 1
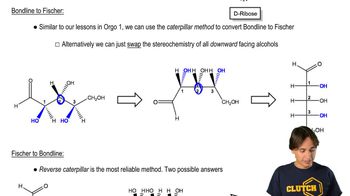
Fischer Projections
Fischer projections are a two-dimensional representation of three-dimensional organic molecules, particularly useful for depicting the stereochemistry of carbohydrates and amino acids. In a Fischer projection, vertical lines represent bonds that go back into the plane, while horizontal lines represent bonds that come out of the plane. This method allows for easy visualization of the absolute configurations of chiral centers, which is essential for solving the question regarding the stereoisomers of tartaric acid.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - Drawing Fischer Projections
Oxidation and Hydrolysis Reactions
Oxidation and hydrolysis are fundamental chemical reactions that involve the transformation of organic compounds. Oxidation typically involves the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen, while hydrolysis involves the reaction of a compound with water, leading to the breakdown of that compound. In the context of the question, understanding these reactions is vital for tracing the synthesis of tartaric acid from its precursors and determining the configurations of the resulting products.
Recommended video:
Triacylglycerol Reactions: Hydrolysis Concept 3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 9:56m
9:56m