Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. In organic chemistry, isomers can be classified into structural isomers, which differ in the connectivity of atoms, and stereoisomers, which have the same connectivity but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms. The stability of isomers can vary significantly based on their structure, influencing their physical and chemical properties.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism
Heat of Combustion
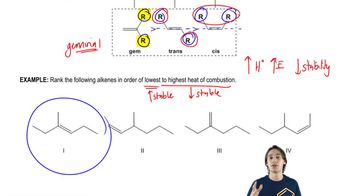
The heat of combustion is the amount of energy released when a substance is completely burned in oxygen. It is an important measure of the stability of a compound; generally, a higher heat of combustion indicates a less stable compound, as more energy is released when it is converted to more stable products. Comparing the heats of combustion of isomers can provide insights into their relative stabilities.
Recommended video:
Steric Strain
Steric strain arises when atoms in a molecule are forced closer together than their preferred distance, leading to increased energy and decreased stability. In cycloalkanes, such as cyclopropane derivatives, steric interactions between substituents can significantly affect stability. The cis isomer of 1,2-dimethylcyclopropane experiences more steric strain due to the proximity of the methyl groups, making the trans isomer more stable despite the higher heat of combustion of the cis isomer.
Recommended video:
What is torsional strain?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution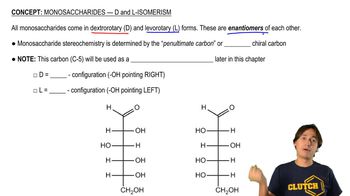


 1:11m
1:11m