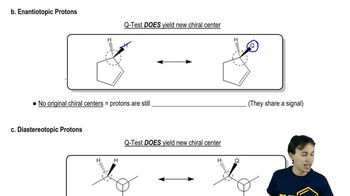
Phenyl Grignard reagent adds to 2-methylpropanal to give the secondary alcohol shown. The proton NMR of 2-methylpropanal shows the two methyl groups as equivalent (one doublet at d 1.1), yet the product alcohol, a racemic mixture, shows two different 3H doublets, one at d 0.75 and one around d 1.0.
<IMAGE>
(a) Draw a Newman projection of the product along the C1–C2 axis.
(b) Explain why the two methyl groups have different NMR chemical shifts. What is the term applied to protons such as these?